Browsing the Signs of Kidney Stones vs UTI: A Detailed Comparison
Comprehending the Secret Distinctions In Between Kidney Stones and Urinary Tract Infections: An Extensive Review for People
Comprehending the differences in between kidney stones and urinary system tract infections (UTIs) is necessary for individuals who might be experiencing similar symptoms yet face greatly various wellness obstacles. While both conditions can show up discomfort in the reduced abdomen or back, their hidden reasons, analysis strategies, and treatment methods diverge considerably. A nuanced understanding of these differences not just help in precise self-assessment but additionally notifies discussions with doctor. As we explore these essential aspects, it becomes clear that acknowledging the special qualities of each problem can profoundly influence patient outcomes. What could be the most effective method to resolving these distinctions?
Overview of Kidney Stones
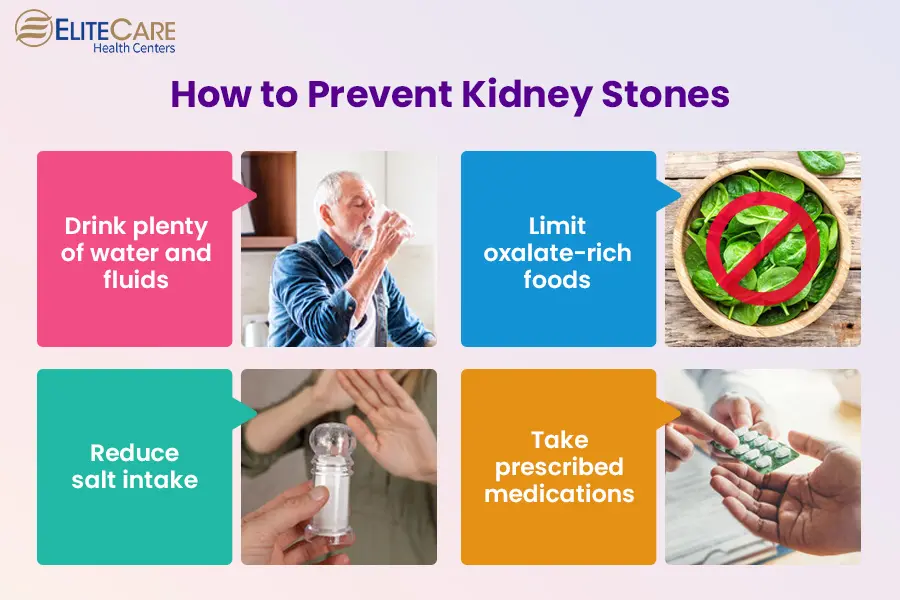
The development of kidney stones, a unpleasant and typically devastating problem, emphasizes the essential value of maintaining renal wellness. Kidney stones, additionally known as kidney calculi, are strong masses that create from crystals in the urine. These stones can vary in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball and can live in any kind of component of the urinary system tract. The primary sorts of kidney stones consist of calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine stones, each with distinctive causes and risk elements.
A number of elements add to the development of kidney stones. Dehydration is a considerable risk, as insufficient liquid intake can lead to focused urine, advertising crystal formation. Nutritional practices, including high sodium and oxalate usage, can intensify the threat. Furthermore, metabolic problems and particular clinical problems may predispose people to stone development.
Signs and symptoms of kidney stones can include severe flank nausea, pain, and hematuria, which usually trigger immediate medical examination. Therapy alternatives differ, ranging from enhanced fluid intake and dietary adjustments to medical treatments such as lithotripsy or medical elimination, depending on the dimension and location of the stones. Recognizing these facets is vital for effective prevention and management.
Introduction of Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary system system infections (UTIs) represent a typical yet significant health and wellness problem, affecting numerous individuals annually. These infections occur when germs get in the urinary system, which consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The majority of UTIs are brought on by Escherichia coli, a kind of microorganisms typically located in the gastrointestinal system. While UTIs can influence any person, they are particularly widespread in ladies due to anatomical differences that help with bacterial entry.
The risk elements for creating a UTI include sexual task, specific types of birth control, urinary system retention, and a history of previous infections. Straightforward UTIs are normally limited to the bladder and are more common in healthy and balanced people, while complex UTIs may include the kidneys and take place in those with underlying health concerns.
Prompt medical diagnosis and treatment are necessary to avoid issues, such as recurring infections or kidney damage (Kidney Stones vs UTI). Typically, UTIs are treated with antibiotics, and safety nets can be used for those with constant incidents
Common Symptoms Comparison
Signs and symptoms of urinary system infections and kidney stones can often overlap, leading to confusion in medical diagnosis. Both conditions can present with discomfort in the lower abdominal area or back, yet the nature and area of the pain commonly vary. In urinary system tract infections (UTIs), individuals generally experience a burning experience during peeing, regular prompts to urinate, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine. In comparison, kidney stones have a tendency to create extreme, pain that emits from the back to the lower abdomen and groin, typically referred to as colicky discomfort.
Additionally, UTIs may be gone along with by high temperature and cools, especially in much more serious situations, while kidney stones can lead to nausea or vomiting and vomiting due to extreme discomfort. While pain throughout urination is a trademark of UTIs, kidney stones generally provide visit this page with even more acute discomfort episodes, which might go and come.
Medical Diagnosis Approaches
Exactly how can health care professionals precisely distinguish between kidney stones and urinary system tract infections? The analysis procedure starts with a detailed clinical history and a thorough testimonial of the client's symptoms. Clinicians usually execute a checkup, which might expose inflammation in the abdominal area or flank area, guiding the diagnostic path.
Lab examinations play a crucial function redirected here in differentiating in between these 2 conditions. Kidney Stones vs UTI. A urinalysis can recognize the presence of blood, crystals, or germs, which are a measure of either condition. In instances of urinary tract infections, the urinalysis might reveal a significant presence of leukocyte and nitrites, while kidney stones might offer with details crystals
Imaging research studies, such as stomach ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) checks, are important for visualizing kidney stones. These imaging methods enable health care companies to assess stone size, place, and prospective obstructions in the urinary system system. On the other hand, urinary system infections normally do not need imaging unless complications are suspected.
With each other, these analysis techniques equip medical care specialists to accurately detect and separate in between kidney stones and urinary tract infections, making sure that individuals get appropriate treatment and administration.
Therapy Options and Prevention
While both kidney stones and urinary system tract infections (UTIs) require punctual treatment, their monitoring methods differ significantly.
The therapy for kidney stones typically includes discomfort administration, hydration, and in some cases, medical treatments such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) or ureteroscopy to damage or eliminate down stones. People are frequently suggested to raise liquid intake to help with stone read the article flow and decrease recurrence. Dietary adjustments might also be required, relying on the stone type.
On the other hand, UTIs are primarily treated with antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection. The particular antibiotic prescribed relies on the microorganisms identified and neighborhood resistance patterns. Additional measures, such as raised liquid intake and urinary analgesics, may aid relieve signs and symptoms.
Prevention approaches differ also; for kidney stones, preserving appropriate hydration and adhering to dietary constraints can be efficient. For UTIs, preventative strategies include appropriate health methods, peing after intercourse, and possibly prophylactic anti-biotics for reoccurring infections. Recognizing these therapy and prevention modalities is vital for efficient administration and to minimize the threat of problems associated with both problems.
Conclusion

Comprehending the differences between kidney stones and urinary system infections (UTIs) is vital for people who may be experiencing similar signs yet encounter vastly different health and wellness obstacles. The primary types of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine stones, each with unique reasons and threat factors.